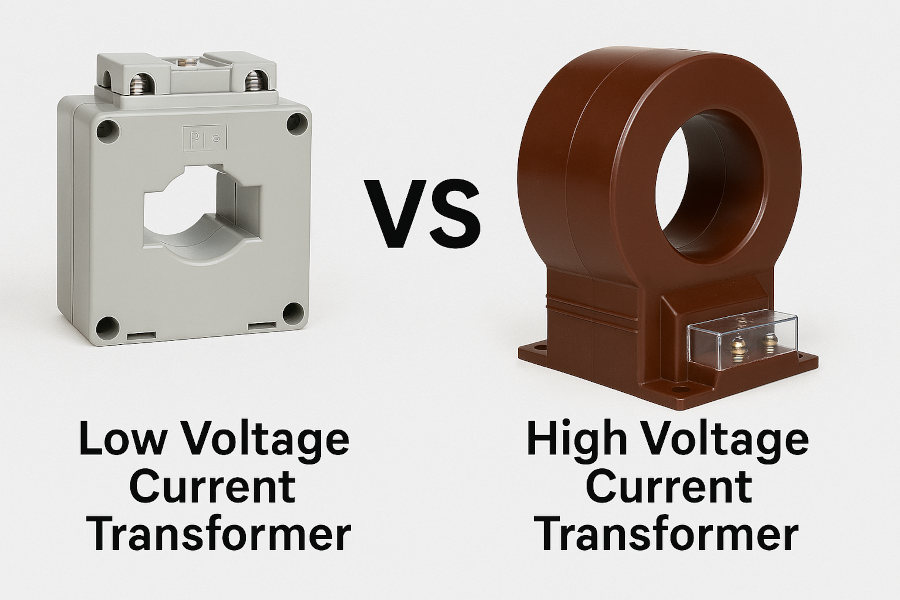
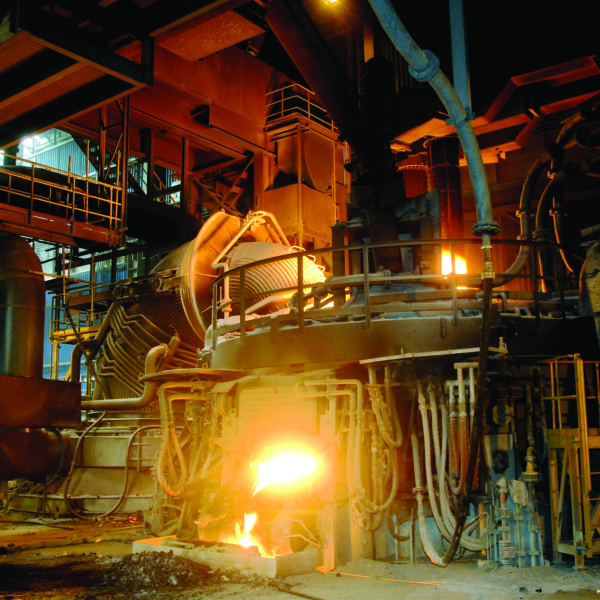
Current transformer, abbreviated as (CT), is a device used for measuring alternating current. It converts large current into a smaller current through the principle of electromagnetic induction, making it convenient for measurement, protection and control. Low-voltage current transformers and high-voltage current transformers are mainly distinguished based on their working voltage levels. Low-voltage current transformers are typically used in power systems with an alternating voltage of 1000V (1kV) or below. High-voltage current transformers are used in ultra-high voltage power grids ranging from 1kV to 100kV.
| Low Voltage CT | High Voltage CT | |
| Voltage Level | It is typically applicable to low-voltage systems of 1kV and below (such as 0.4kV, 0.66kV). | It is suitable for high voltage systems above 1kV (such as 10kV, 35kV, 110kV or even higher). |
| Insulation level | The insulation requirements are relatively low, and dry insulation (such as epoxy resin casting or air insulation) is often used, with a low withstand voltage. | High insulation requirements are required, and oil-immersed, SF6 gas insulation, or composite insulation are often used to withstand high voltage and prevent breakdown. |
| Structural design | It has a simple structure, small size, and light weight, and is usually a ring or rectangular iron core, making it easy to install. | The structure is complex and the volume is large, which may include porcelain sleeves, oil tanks or gas chambers to ensure safe isolation. |
| Application | It is widely used in low-voltage distribution cabinets, industrial control systems, metering instruments, and household appliance protection. | It is widely used in high-voltage substations, transmission lines, and power plants for measurement, protection relays, and fault monitoring. |
| Safety and Maintenance | It is easy to install and maintain, has low cost, and low risk. | It has strict safety requirements, is complex to maintain, requires regular inspection of insulating oil or gas, and is costly. |
| Standards and Specifications | It complies with standards such as IEC 61869-2, but focuses on low-voltage safety. | It complies with standards such as IEC 61869-2, emphasizing high-voltage insulation and shock resistance. |






Copyright © 2024 PowerUC Electronics Co.